How Informal Mentoring by Teachers, Counselors, and Coaches Supports Students’ Long-Run Academic Success
Abstract:
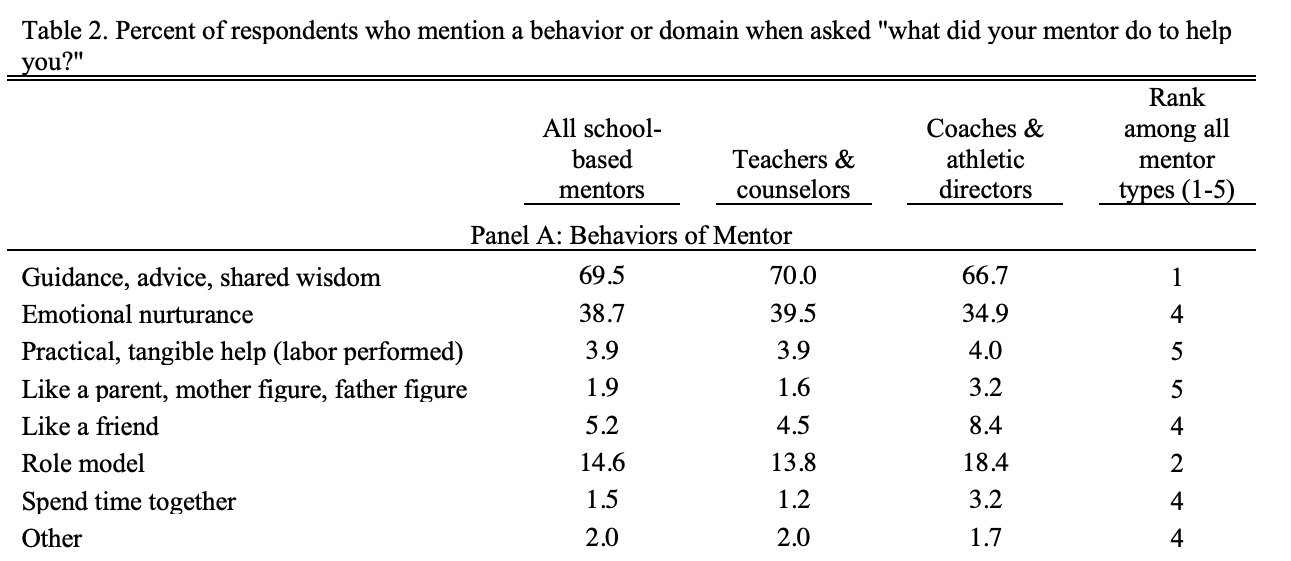
We document a largely unrecognized pathway through which schools promote human capital development – by fostering informal mentoring relationships between students and teachers, counselors, and coaches. Using longitudinal data from a nationally representative sample of adolescents, we explore the nature and consequences of natural mentoring relationships by leveraging within-student variation in the timing of mentorship formation as well as differences in exposure among pairs of twins, best friends, and romantic partners. Results across difference-in-differences and pair fixed-effect specifications show consistent and meaningful positive effects on student attainment, with a conservative estimate of a 9.4 percentage point increase in college attendance. Effects are largest for students of lower socioeconomic status and robust to controls for individual characteristics and bounding exercises for selection on unobservables. Smaller class sizes and a school culture where students have a strong sense of belonging are important school-level predictors of having a K-12 natural mentor.
Citation:
Kraft, M.A., Bolves, A. & Hurd, N. (2023). How Informal Mentoring by Teachers, Counselors, and Coaches Supports Students’ Long-Run Academic Success. Economics of Education Review, 95, 102411